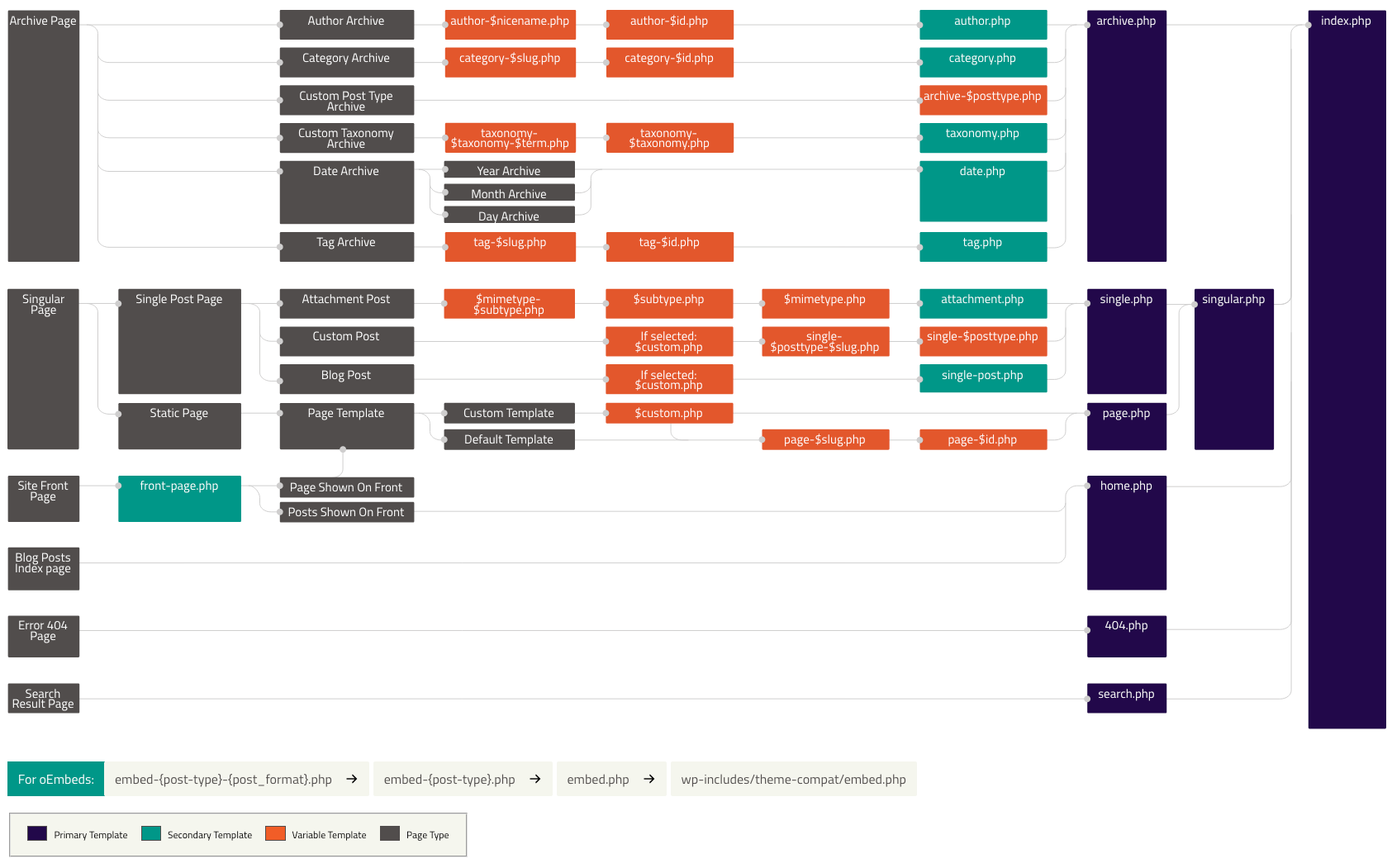
When diving into WordPress theme development, one of the first concepts you’ll encounter is the Template Hierarchy. It may seem intimidating at first, but once you understand how WordPress decides which template file to use for different types of content, you’ll have much more control over how your site looks and behaves.
In this guide, we’ll break down the WordPress Template Hierarchy in a way that’s simple, visual, and practical — perfect for beginners.
What is the WordPress Template Hierarchy?
The Template Hierarchy is the system WordPress uses to determine which theme file to use when displaying a page. It’s like a flowchart that tells WordPress:
“If the user is viewing a single post, use this file. If that doesn’t exist, use this other one.”
WordPress checks for files in a specific order until it finds a match. This helps developers override only the parts of the theme they want to change without affecting the entire site.
Why Should You Care?
Knowing the Template Hierarchy helps you:
- Customize specific pages without touching global templates.
- Build more modular and maintainable themes.
- Fix layout or display issues quickly.
- Create a better user experience.
The Template Hierarchy in Action (Examples)
Let’s go through some common scenarios.
1. Single Post Page
When viewing a single blog post, WordPress looks for templates in this order:
single-{post-type}-{slug}.php
single-{post-type}.php
single.php
singular.php
index.php
Example:
For a post with slug travel-tips, it checks:
single-post-travel-tips.phpsingle-post.phpsingle.php- …
2. Page (Static Page)
For a WordPress page, it checks:
page-{slug}.php
page-{id}.php
page.php
singular.php
index.php
Example:
For a page called “Contact”, WordPress will look for:
page-contact.phppage-42.php(if the page ID is 42)page.php
3. Category Archive
For category archives, WordPress checks:
category-{slug}.php
category-{id}.php
category.php
archive.php
index.php
Example:
For a category named “News”:
category-news.phpcategory-7.php(if the ID is 7)category.php
4. Search Results
search.php
index.php
5. 404 Page (Page Not Found)
404.php
index.php
Visual Representation
Imagine the hierarchy like a pyramid, with the most specific template at the top, and the most general (index.php) at the base. WordPress always starts from the top and falls back down until it finds a match.
Pro Tips for Developers
- Use Template Partials: Instead of repeating code, split templates into reusable parts like
header.php,footer.php,sidebar.php. - Don’t Forget
get_template_part(): Load specific sections cleanly and conditionally. - Always Have an index.php: It’s the fallback file. Without it, WordPress may break.
Wrapping Up
Understanding the WordPress Template Hierarchy is essential for any theme developer. It empowers you to create precise customizations while maintaining clean, organized code.
Start experimenting by creating custom templates for your pages, posts, and categories — you’ll be amazed how much control you have over your site’s layout.







2 thoughts on “Understanding the WordPress Template Hierarchy: A Beginner’s Guide”
Even after years of using WordPress, I always get confused with the template structure. This guide cleared things up — bookmarking this one!
Super helpful! Could you also write a guide on how to override specific templates in a child theme? That’s something I’ve been struggling with.