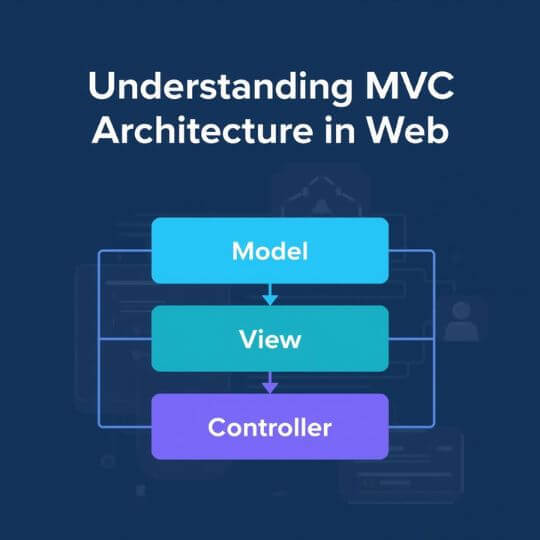
When diving into web development—whether you’re working with PHP frameworks like Laravel, JavaScript environments like Node.js, or even WordPress plugin architecture—understanding the MVC architecture is a game changer. MVC stands for Model-View-Controller, and it’s a design pattern that helps developers organize code in a scalable, maintainable way.
Let’s explore what MVC is, how it works, and why it matters in modern web development.
What is MVC?
MVC stands for:
- Model – Manages the data and business logic.
- View – Handles the user interface and presentation.
- Controller – Receives input, processes it (often via the model), and returns a view.
This architectural pattern separates concerns, making your application easier to manage, scale, and debug.
How MVC Works: A Simple Flow
Here’s what typically happens in an MVC-based application:
- The user sends a request (e.g., clicking a button or submitting a form).
- The controller captures the request and interacts with the model to process any data.
- The model performs operations (e.g., fetch from a database) and returns the result.
- The controller then sends this data to the view, which formats it for display.
- The view renders the content and returns it to the user.
MVC Components Explained
1. Model
The model is responsible for:
- Managing application data
- Interacting with the database
- Defining business logic
Example: In a blog app, the model would handle retrieving and saving blog posts.
2. View
The view:
- Displays the data to the user
- Receives data from the controller
- Can be HTML, JSON, or any presentation layer
Example: A blog template that displays a list of posts or a single post layout.
3. Controller
The controller:
- Responds to user input
- Acts as a bridge between the model and the view
- Processes business logic and decides which view to show
Example: In a blog, the controller would determine if a user is viewing all posts or a single post and pull the right data from the model.
Benefits of MVC in Web Development
- ✅ Separation of Concerns
Each part of the application (logic, interface, data) is managed separately. - ✅ Maintainability
Easy to make changes without affecting the whole system. - ✅ Scalability
You can scale components independently (e.g., modify only the view for a new theme). - ✅ Reusability
Logic in models and controllers can be reused across multiple views.
Where is MVC Used?
MVC is used in almost every major web framework today:
- Laravel (PHP)
- ASP.NET MVC
- Ruby on Rails
- Django (uses MTV—Model Template View, but similar)
- Spring MVC (Java)
- Express.js + MVC structure (Node.js)
- Even WordPress plugins and themes can be structured following MVC for better modularity
MVC vs Other Architectures
While MVC is popular, it’s not the only architectural pattern. Others like MVVM, MVP, or Component-based architectures (like in React) are also widely used. But MVC remains one of the most intuitive and beginner-friendly ways to learn structured app development.
Conclusion
Understanding MVC is essential for any web developer aiming to build clean, maintainable, and scalable applications. Once you get the hang of MVC, you’ll find it easier to work with frameworks, debug code, and architect your own projects with confidence.
Whether you’re building your first CRUD app or refactoring a WordPress plugin, think in terms of Model, View, and Controller—you’ll thank yourself later.